An Overview on Proximity Sensors
Proximity Sensors – Different types, Functionalities, Applications and Market trends
There are many different types of sensors available today in the electronics market. Our focus in this discussion is a type of sensor technology called a proximity sensor. We will explain how proximity sensors work, the various types, and what these sensors are used for. We will also cover the increasing relevance of this technology as we move forward into the future.
What are proximity sensors?
Proximity sensors detect how far away a target (object being measured) is without physical contact.
How do proximity sensors work?
Depending on the type of proximity sensor, it will either emit an electromagnetic field, infrared radiation, sound or light beam. Once the beam/field is emitted from the sensor, it looks for any differences and changes in the return signal and then can determine the distance of the target.
What are proximity sensors used for?
They can be found in many different applications including, but not limited to, autonomous cars, smart phones, aircrafts, smart factories, etc.
What are the different types of proximity sensors?
There are many different types including inductive proximity sensors, magnetic proximity sensors, capacitive proximity sensors, photoelectric proximity sensors, and ultrasonic proximity sensors.
Inductive Proximity Sensors
This type of sensor is best used for detecting metal. The sensor can detect the distance of any metal object within the magnetic field.
Inductive proximity sensors are frequently built into metal fixtures. To prevent the sensor from detecting that metal fixture these applications require a shielded inductive proximity sensor.
Shielded inductive sensors increase the accuracy of the sensor but compromise on range. Unshielded inductive sensors have longer range but can not be mounted on or in certain metals.
Inductive proximity sensors are commonly used in industrial and military applications. One use case for the military is landmine detection.
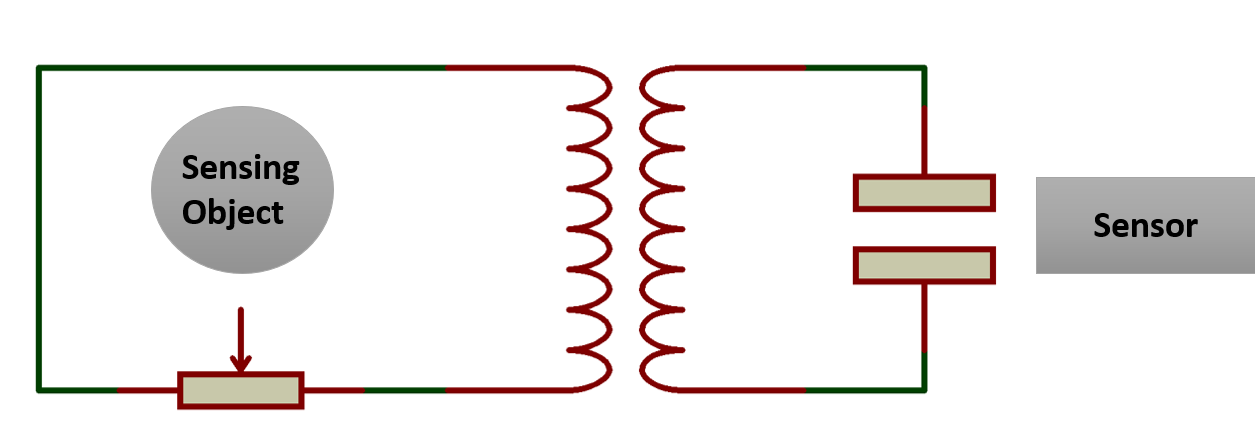
Figure 1 : Inductive Proximity Sensor Diagram
Magnetic Proximity Sensors
This type of sensor can detect a variety of materials including metals, plastics and wood. These sensors includes a reed switch that detects nearby magnets. The reed switch makes contact when it nears a magnet and alerts the sensor.
These sensors are commonly used in large data/server centers and also in clean energy applications such as wind turbines and solar panels.
Capacitive Proximity Sensors
This type of sensor is able to detect metals and non-metals. Capacitive proximity sensors use two conduction plates that work like an open capacitor with air in between them. When something enters the sensors field, capacitance occurs and the system is alerted.
Capacitive proximity sensors are commonly used in industrial applications, specifically in automated production lines where they help in operating machine systems and positioning moving parts.
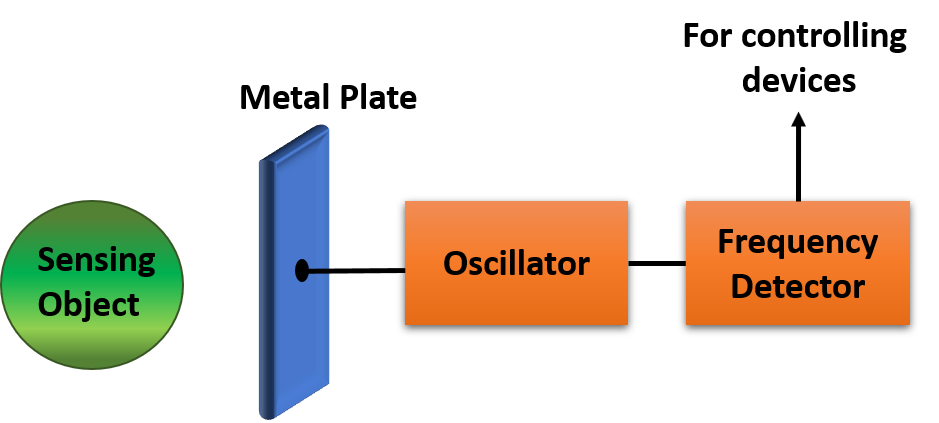
Figure 2: Capacitive Proximity Sensor
Photoelectric Proximity Sensors
This sensor works very well in areas where there are a lot of airborne contaminants. They work by emitting visible/invisible light to a receiver. If the beam of light is blocked, and the receiver detects a disruption or total blockage in the light beam, the system is alerted. Systems can either be alerted when light is received or when it is not received, depending on whether the sensor is a dark-on or light-on sensor.
These sensors are commonly used for automated doors, detecting colors, materials/ logistic applications, and for counting small objects.
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
This type of sensor emits sound waves from a transducer at very high frequencies. The sensor waits for the sounds to be reflected back and based on the time period, the sensor can accurately determine the distance of the target.
This type of sensor is used in self parking technology, anti-collision systems, manufacturing, and obstacle detection.
Proximity Sensor Market
The proximity sensor market in 2019 was valued at $2.94 billion and is projected to reach $4.45 billion by 2025, growing at a rate of 7% year over year.
Much of this growth is a result of increasing investment in automation hardware. This includes the likes of healthcare, industrial, automotive and smartphone markets.
Automotive markets are predicted to carry the largest amount of market share. We see a few different applications of proximity sensors in these markets.
For a touch-free user experience auto companies are equipping their vehicles with proximity sensors that allow keyless entry, 3D passenger modeling and interior lighting control. Proximity sensors are also being used in vehicles for parking assistance, anti-collision and fully autonomous driving systems.
Lastly, we also expect to see a significant increase of proximity sensors in the smartphone market. Many smartphones already have proximity sensors. Their main purpose is to conserve battery life by turning the display screen on or off based on your distance to the phone. For instance, you may notice how your smartphone turns its display off when the phone is placed up to your ear, or turns its display on when you’re looking at the screen.
In fact, Apple has created technology with proximity sensors that detects when your phone is falling, and prepares itself for an impact.
Clearly the applications for proximity sensors are seemingly endless. These are just a few examples of how they are being used today. As innovative technologies and products continue to be developed, we can expect exponential market growth.
Browse and Shop Sensors
Find more articles like this on our Blog

