Tantalum Capacitors – Overview and Explanation
Tantalum Capacitors
Capacitor Overview
- In an electric circuit, the capacitor is a passive, two terminal device that can statically store electric energy between it’s terminals by using a technique called charge separation. The charge separation phenomenon occurs in capacitors due to the dielectric material placed between its metal plates. The capacitance (C) , the fundamental effect of capacitor, is measured in farads (F) which is named after the English scientist Michael Faraday. The capacitance of a capacitor is equal to one farad (F) when one coulomb (Q) of electric charge changes the electric potential between the plates by one volt (V). Capacitance is expressed by the equation in Figure 1.
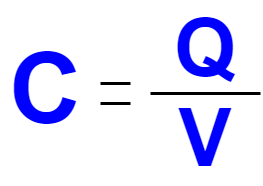
Figure 1: Capacitance Equation
- It is important to note that, there are also both fixed and variable capacitors similar to the case with resistors. Capacitors that have fixed values can be grouped into two categories with respect to their polarity as non-polarized and polarized capacitors. Electric symbols of the three most commonly used capacitor types are represented in Figure 2.
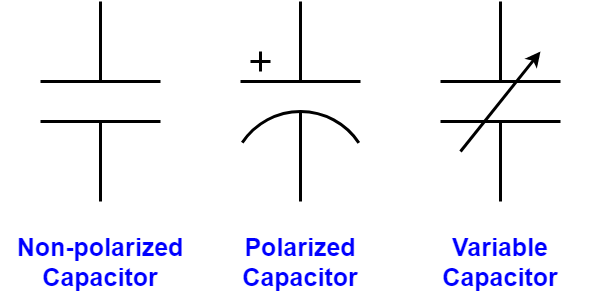
Figure 2: Capacitor Symbols
Definition of the Tantalum Capacitor
- As mentioned in the previous section, fixed and variable capacitors have different electric symbols and operation principles. Capacitors having fixed value of capacitance can be categorized into two groups as polarized and non-polarized capacitors. Polarized capacitors have asymmetrical construction and always must be operated with a higher voltage on the positive terminal (anode) than on the negative terminal (cathode). Polarized capacitors can also be grouped into two categories as electrolytic and super capacitors. An electrolytic capacitor’s positive (anode) plate is made of a special metal that forms an oxide layer. Then the oxide layer operates as the dielectric of the electrolytic capacitor through anodization. A liquid, gel or solid electrolyte covers the surface of oxide layer and behaves as the negative (cathode) plate of the electrolytic capacitor. The three families of electrolytic capacitors aluminum, tantalum and niobium are shown in Figure 3.
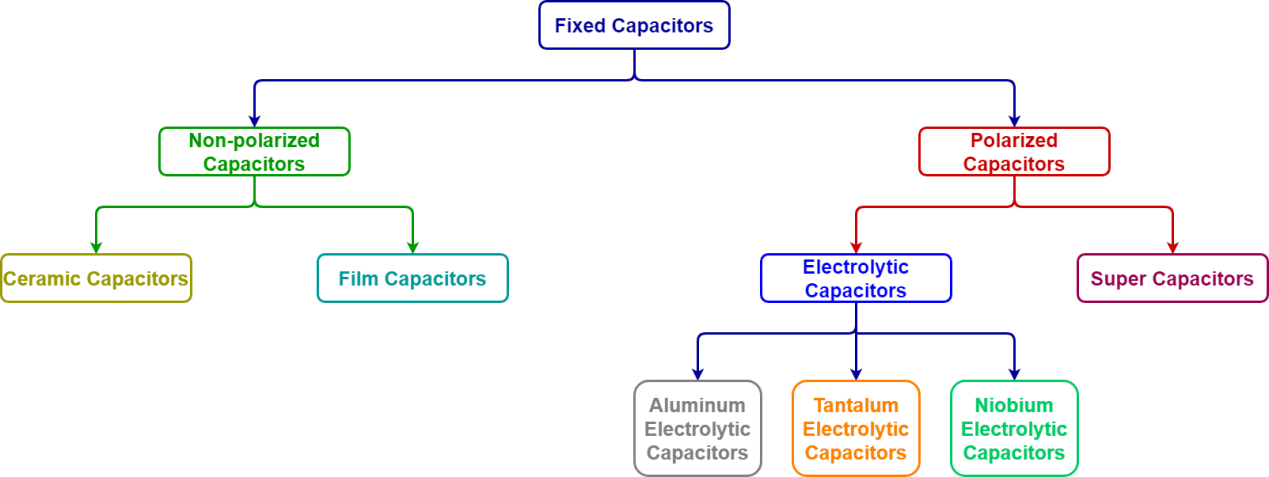
Figure 3: Types of Capacitors
- Without any doubt, the tantalum electrolytic capacitor is one of the most prevalent types of capacitors due to its much higher charge capacity than film or ceramic capacitors. Tantalum electrolytic capacitors have also less leakage and higher frequency response than aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Therefore, tantalum electrolytic capacitors are preferred in various electronic applications where small size and higher operation frequencies are needed. The niobium electrolytic capacitor is also an alternative to tantalum electrolytic capacitors and started to drawing more and more attention at the huge capacitor market due to its safety features such as higher flame retardation.
Construction of a Tantalum Capacitor
- Tantalum (Ta) is a bright, silver-gray metal element with the atomic number 73. When the cross-sectional view of the tantalum capacitor is examined such as a typical SMD tantalum electrolytic chip capacitor with solid electrolyte shown in Figure 4, it consists of tantalum powder pressed and sintered into a pallet as the positive (anode) terminal of the chip capacitor. The positive (anode) terminal is covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric and the solid manganese dioxide electrolyte acts as the negative (cathode) terminal.
- Tantalum capacitors have high capacitance per volume and weight, because of their thin and relatively high permittivity dielectric layer which distinguishes itself from other electrolytic capacitors. Therefore, the large capacitance of tantalum electrolytic capacitors makes them suitable for passing or bypassing low-frequency signals, and storing large amounts of electric energy.
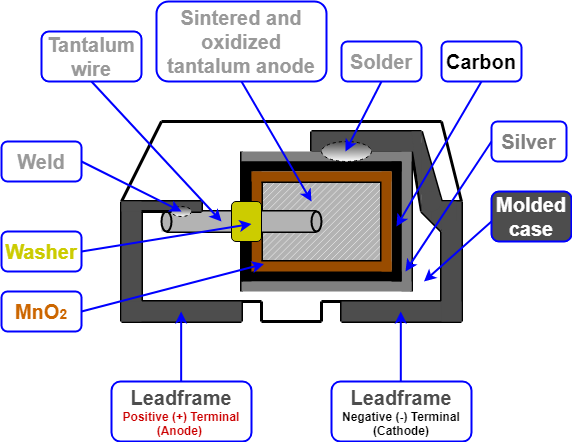
Figure 4: SMD tantalum electrolytic chip capacitor with solid electrolyte
Applications of Tantalum Capacitors
- Capacitors appear in all types of electronic devices from TVs, radios, computer equipment, Wi-Fi routers to mobile phones. Obviously, any piece of electronic equipment has several capacitors inside and those capacitors come in all shapes and sizes. Capacitors are produced using various methods of construction and dielectric materials that considerably affect their performances. Since some types of capacitors work better in some applications than others, understanding the differences between the different types of capacitors is extremely important.
- Tantalum capacitors are one of the most popular capacitor types in the microelectronics industry. More than 80% of all tantalum electrolytic capacitors are manufactured in surface mount device (SMD) style as tantalum electrolytic chip capacitors. However, niobium based electrolytic capacitors are also getting popular in electronics industry due to abundance of the niobium element in nature. Nowadays, the energy conservation requirements for capacitors is increasing due to the demand for low power applications. Since the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of a tantalum electrolytic capacitor is relatively low, they are still very popular in electronic application where energy saving is vital.
Shop Tantalum Capacitors
Read our other articles from our Blog

